
E-commerce is growing around the globe. Consumers are using their smartphones to make purchases increasingly often. Population growth in the emerging markets and the associated expansion of the middle class are driving sales in the consumer goods sector. The rising number of internet users is accelerating the development of online sales. Increasing urbanization is supporting consumption growth by providing easy access to products and shorter delivery distances.
The e-commerce market
The e-commerce market
Technical advances, growing convenience for consumers, and a wider range of offers thanks to online channels are boosting the trend towards e-commerce:
- Global e-commerce sales currently stand at around USD 1,800 billion a year.
- These sales today account for a high single-digit percentage of total global retail sales.
- Around half of these sales are processed via mobile phone apps, so-called m-commerce (mobile commerce), with revenue in this area rising.
- We anticipate annual growth for the overall market of between 15% and 20% for the next ten years.
- Online retailers are currently expanding their presence strongly in the emerging markets, where responding to local circumstances is key to success.
Important growth factors for e-commerce
Important growth factors for e-commerce
- The technical development of personal computers and mobile phones is very rapid. Affordable prices are promoting the penetration of the internet and smartphones, especially in the emerging markets. Faster internet connections and user-friendly mobile apps are also enhancing the online shopping experience.
- Consumers are embracing this unrestricted availability as a welcome source of convenience. Where they are and what time of day it is are of no significance. Prices can be compared simply and without great effort, and the delivery of goods directly to their home is quick and convenient. Thanks to advanced payment technologies, paying is now simple and secure.
- Using online businesses and marketplaces lets companies expand their product offering in a cost-effective manner. There is no need for additional business premises. The cross-border online market is continuing to increase in significance. Consumers are benefiting from an expanded offering.
Barriers to entry
Barriers to entry
The technical building of an online business does not need extensive investment. However, capital is required for the start-up phase as well as significant investment in order to gain the acceptance of clients. The following barriers to entry need to be taken into account:
- Economies of scale: The greater the volume, the lower the costs. New competitors are thus required to challenge existing market players in terms of price, or offer better quality at a good price.
- Market recognition: Consumers chiefly opt for known online marketplaces. Established providers benefit from the recognition factor. New competitors must work hard to develop their brand and the recognition factor.
- Product differentiation: Clients demand a large and broad product offering. So good relationships with manufacturers are decisive for new competitors. Generally, significant price concessions are necessary.
- Technology: User-friendliness is key for online marketplaces. Established e-commerce firms are thus investing in expensive big data solutions.
- Logistics and delivery options: The "last mile" of the delivery process is critical. Experienced e-commerce companies are already testing new delivery technologies. New competitors with smaller volumes must either develop their own delivery network or call on the services of local distribution partners. Both are expensive.
E-commerce investment opportunities
E-commerce investment opportunities
The e-commerce market is very diverse. We currently see long-term investment opportunities in connection with the following topics.
- Electronic marketplaces: Online platforms bring together the buyers and providers of products and services.
- Pure online retailers: Companies that exclusively sell their products online.
- Multi-channel retailers: Companies that distribute their goods via several sales channels such as shops, online platforms and mobile platforms.
- Logistics operators: The growing acceptance enjoyed by e-commerce depends on an efficient distribution and warehouse networks.
- Payment service providers: In addition to traditional credit card companies, new firms are also offering payment systems for online transactions.
- Price comparison platforms: Companies that ensure greater price transparency and compare different providers with one another.
Network operators: Telecommunication firms provide the technology and infrastructure that make e-commerce possible in the first place. In the short term, however, telecommunication companies are not among the main beneficiaries of e-commerce, as they have to invest in quick, good and stable connections.
- Cyber security: The growth of e-commerce depends on secure hardware and software to ensure that clients do not fall victim to internet crime when making online transactions.
E-commerce is currently dominated by the IT and service sector.
E-commerce is currently dominated by the IT and service sector.
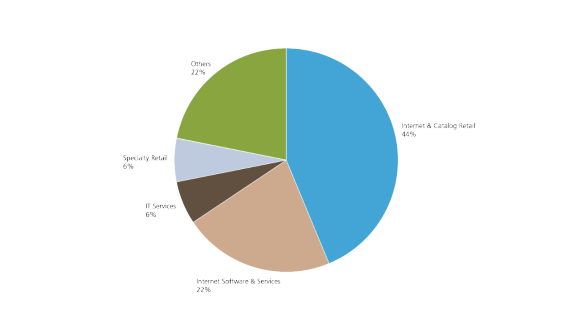
Investments in e-commerce are attracting a high level of attention worldwide. The emerging markets, in particular, offer very good growth opportunities. The market is very diverse, with companies that offer a wide range of products and services.
Are you interested in a long-term investment in e-commerce retail? This is exactly what our long-term investment fund offers. Our experts have identified interesting investment opportunities for you. Invest with us in a modern and efficient future. With UBS Manage or UBS Advice, you can benefit from our tailored solutions for long-term investments.

